When it comes to medical care, the Ryles tube is a versatile device with a wide range of applications. From providing nutrition to administering medications and facilitating gastric decompression, this tube plays a crucial role in enhancing patient well-being. Let’s explore some of its key uses.
Key Takeaways:
- The Ryles tube is used for feeding, medication delivery, gastric decompression, and more.
- It provides nutrition to patients who are unable to eat or swallow.
- The tube acts as a conduit for administering medications and supplements.
- It helps alleviate gastric distension and removes excess air or fluids from the stomach.
- Gastric residuals can be monitored using a Ryles tube to adjust feeding regimens.
Feeding through a Ryles Tube
Feeding through a Ryles tube plays a crucial role in providing nutrition to patients who are unable to eat or swallow. This procedure allows healthcare professionals to ensure that patients receive the essential nutrients they need for their recovery or overall well-being.
The process of inserting a Ryles tube for feeding involves careful placement and monitoring to ensure successful nutrition delivery. The tube is gently guided into the patient’s stomach, bypassing the mouth and esophagus. Once in place, it can be used to administer liquids, semi-solids, or even medication directly into the stomach.
Feeding through a Ryles tube requires proper care and attention to maintain its effectiveness. Regular flushing of the tube with water or medication can help prevent clogs or blockages, ensuring a consistent and reliable flow of nutrients to the patient.
“Feeding through a Ryles tube provides vital nourishment to patients who cannot eat or swallow. It offers a controlled and reliable method of delivering essential nutrients, aiding in their recovery and overall health.”
Ryles Tube Feeding Care Guidelines
When caring for a patient with a Ryles tube for feeding, it is essential to follow specific guidelines to ensure their comfort and safety:
- Regularly check the position of the tube to ensure it remains properly placed in the stomach.
- Administer prescribed medications or supplements as directed by the healthcare provider.
- Use only appropriate types of liquids or foods suited for Ryles tube feeding.
- Monitor for any signs of infection, irritation, or complications at the insertion site.
- Regularly clean and flush the tube to prevent clogs and maintain its functionality.
By adhering to these care guidelines, healthcare professionals can help ensure the successful and safe delivery of nutrition through a Ryles tube, promoting the patient’s well-being and overall recovery.
| Benefits of Feeding through a Ryles Tube | Concerns or Considerations |
|---|---|
| Allows patients to receive essential nutrition despite the inability to eat or swallow | Potential risks of infection or irritation at the insertion site |
| Provides a controlled and reliable method of delivering consistent nutrition | Possible clogs or blockages in the tube, requiring regular flushing |
| Aids in the recovery and overall health of patients with nutritional deficiencies | Requires close monitoring to ensure proper placement and functioning |
Medication Delivery via Ryles Tube
When it comes to medication delivery, the Ryles tube proves to be a valuable tool in medical practice. This flexible tube provides a safe and efficient conduit for administering medications and supplements directly into the stomach. By bypassing the oral route, healthcare professionals can ensure effective delivery and absorption of the required medications, even in patients with impaired swallowing or gastrointestinal issues.
There are several advantages to utilizing a Ryles tube for medication delivery:
- The ability to deliver medications in liquid form, ensuring accurate dosage and minimizing the risk of aspiration.
- Reduced dependency on oral intake, especially in patients with dysphagia or oral feeding difficulties.
- Enhanced medication absorption, as the medication directly enters the stomach for distribution and systemic effect.
- Increased patient comfort, as the procedure for medication administration via a Ryles tube is generally well-tolerated.
However, it is crucial to consider certain factors to ensure safe and effective medication delivery via a Ryles tube. Prior to administering any medications, a healthcare professional should:
- Verify the compatibility of the medication with enteral feeding formulations.
- Ensure the medication is adequately crushed and dissolved for proper delivery through the tube.
- Follow proper flushing protocols before and after medication administration to prevent clogging and ensure tube patency.
- Check for any signs of gastrointestinal intolerance or adverse reactions to the medication.
- Regularly assess the patient’s response and adjust medication dosage or schedule as necessary.
By adhering to these considerations, healthcare professionals can optimize medication delivery via a Ryles tube, providing patients with the necessary medications while minimizing potential risks and complications.
Medication delivery via a Ryles tube offers a convenient and effective alternative for patients who cannot take medications orally. With proper care and attention, this method ensures accurate dosage and improved medication absorption, ultimately enhancing patient care and treatment outcomes.
| Advantages of Medication Delivery via Ryles Tube |
|---|
| Accurate dosage administration |
| Improved medication absorption |
| Reduced dependency on oral intake |
| Enhanced patient comfort |
Gastric Decompression with a Ryles Tube
When it comes to alleviating gastric distension and removing excess air or fluids from the stomach, a Ryles tube plays a crucial role. Gastric decompression using a Ryles tube is a procedure commonly employed in medical care settings to provide relief and improve patient comfort.
The process involves the insertion of a Ryles tube through the nose or mouth and down into the stomach. This tube is specifically designed with a decompression lumen, allowing the healthcare professional to safely release built-up pressure and excess fluids from the gastrointestinal tract. By emptying the stomach, gastric decompression can help alleviate symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and bloating.
Indications for gastric decompression with a Ryles tube may include conditions like gastrointestinal obstruction, paralytic ileus, bowel obstruction, or gastric dilation. It can also be used to prepare patients for certain surgical procedures or manage complications following abdominal surgery.
However, it’s important to note that gastric decompression with a Ryles tube is not without potential complications. These may include tube misplacement, aspiration, or injury to the nasal passage or throat. Healthcare professionals must carefully consider patient factors and follow proper insertion and care guidelines to minimize the risks associated with this procedure.
“Gastric decompression using a Ryles tube is a valuable intervention for relieving gastric distension and promoting patient comfort. By removing excess air and fluids from the stomach, this procedure can alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms and improve overall well-being.”
| Advantages of Gastric Decompression with a Ryles Tube | Potential Complications of Gastric Decompression |
|---|---|
|
|
Case Study: Successful Gastric Decompression
Let’s look at the case of Mrs. Johnson, a 61-year-old patient with a history of bowel obstruction. Mrs. Johnson presented with severe abdominal distension, nausea, and vomiting. As part of her treatment, her healthcare team decided to perform gastric decompression using a Ryles tube.
The healthcare professional followed proper insertion and care guidelines, ensuring the tube was securely placed in Mrs. Johnson’s stomach. Over the course of a few hours, gastric decompression resulted in the reduction of abdominal distension, relief of symptoms, and improved patient comfort. Mrs. Johnson’s overall condition improved, allowing her to resume oral intake and continue her recovery.
This case study highlights the efficacy of gastric decompression with a Ryles tube in managing gastric distension and providing relief for patients with abdominal conditions.
In the next section, we will shift our focus to monitoring gastric residuals using a Ryles tube and its significance in patient care.
Monitoring Gastric Residuals using a Ryles Tube
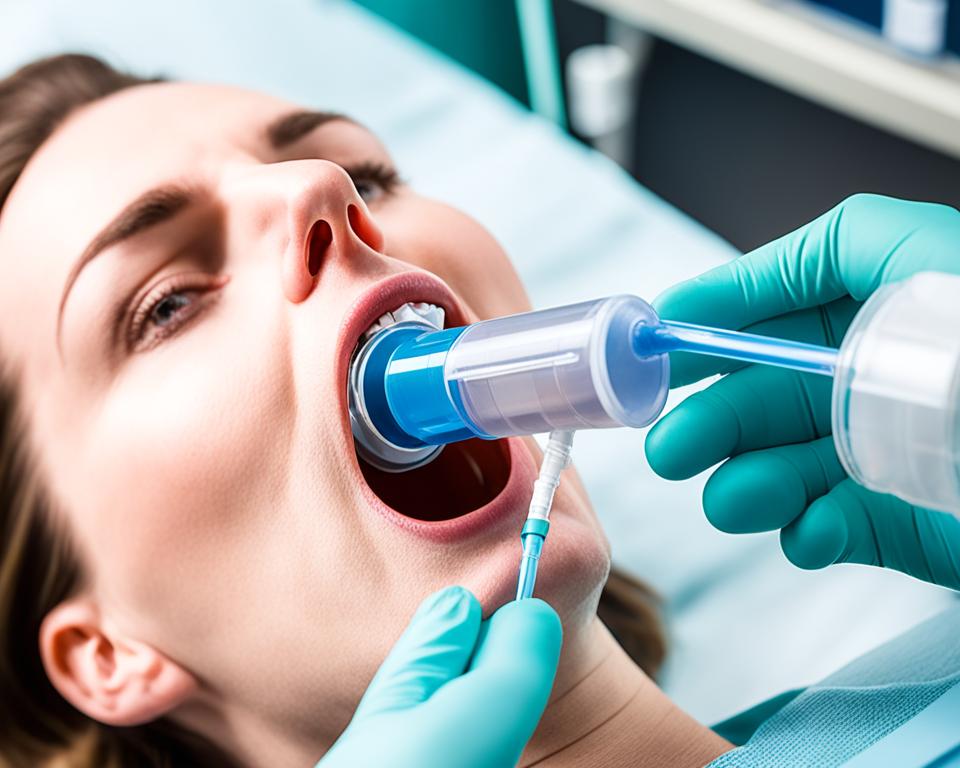
In medical care, the use of a Ryles tube goes beyond feeding and medication delivery. It also serves as a valuable tool for monitoring gastric residuals, providing crucial insights for healthcare professionals to adjust feeding regimens and assess gastrointestinal motility.
Gastric residuals refer to the volume of food or medication left in the stomach after a feeding. By monitoring gastric residuals using a Ryles tube, healthcare providers can gauge digestion and absorption, ensuring optimal nutrition and avoiding complications such as aspiration pneumonia or feeding intolerance.
Measuring gastric residuals using a Ryles tube involves withdrawing the contents of the stomach through gentle aspiration. The obtained volume is then assessed to determine whether the feeding rate or schedule needs modification. This monitoring technique is especially essential for patients with impaired gastric emptying, such as those with gastroparesis or neurological conditions.
Regular monitoring of gastric residuals using a Ryles tube allows healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding feeding adjustments. It enables them to identify potential issues such as delayed gastric emptying or inadequate digestion, which can guide the modification of the feeding schedule, volume, or formulation to optimize patient outcomes.
“Accurate monitoring of gastric residuals using a Ryles tube is a crucial aspect of patient care. It helps us ensure that nutrition is being adequately delivered and that the gastrointestinal system is functioning optimally.” – Dr. Sarah Reynolds, Gastroenterologist
Furthermore, monitoring gastric residuals using a Ryles tube can aid in identifying patients who may benefit from additional diagnostic tests or interventions. Abnormal gastric residuals may prompt further investigations to evaluate gastrointestinal motility disorders or identify potential complications of enteral nutrition.
It is important to note that monitoring gastric residuals alone does not provide a definitive diagnosis or treatment plan. However, it serves as a valuable tool to guide clinical decision-making and optimize patient care. Regular assessment of gastric residuals helps healthcare professionals proactively tailor feeding regimens and promote the well-being of patients reliant on enteral nutrition.
| Benefits of Monitoring Gastric Residuals using a Ryles Tube | Clinical Implications |
|---|---|
|
|
Emergency Situations and Ryles Tube Utilization

In emergency situations, the utilization of a Ryles tube can be a crucial intervention for patients who are unable to tolerate oral intake or require immediate medication administration. The versatility and effectiveness of the Ryles tube make it an invaluable tool in these critical moments.
Protocols and considerations play a pivotal role in ensuring the optimal utilization of the Ryles tube in emergency scenarios. It is essential for healthcare professionals to have a clear understanding of when and how to utilize a Ryles tube, as well as the necessary precautions and safety measures.
In emergency situations where a patient is unable to tolerate oral intake, the Ryles tube provides a reliable alternative for delivering essential nutrition and hydration. By bypassing the oral route and directly accessing the gastrointestinal tract, the tube allows for the continuation of vital sustenance even in challenging circumstances.
Additionally, the Ryles tube facilitates immediate medication administration when time is of the essence. Whether a patient requires life-saving medications or urgent therapeutic interventions, the Ryles tube offers a direct pathway for delivering these medications promptly and efficiently.
“In emergency situations, the utilization of a Ryles tube can be a crucial intervention for patients who are unable to tolerate oral intake or require immediate medication administration.”
Emergency Situations and Ryles Tube Protocols
When utilizing a Ryles tube in emergency situations, several protocols and considerations need to be observed to ensure patient safety and optimize outcomes. These may include:
- Assessing the patient’s medical condition: Before proceeding with Ryles tube insertion, it is critical to thoroughly assess the patient’s overall medical condition, including their vital signs, physical status, and medical history. Emergency procedures should only be performed when medically necessary and appropriate.
- Expertise and training: Healthcare professionals involved in the insertion and management of Ryles tubes should possess the necessary expertise and training to perform these procedures safely. This includes understanding proper insertion techniques, assessing placement, and managing potential complications.
- Emergency response: Establishing a clear emergency response plan is vital to ensure the timely and effective utilization of a Ryles tube. This includes having necessary equipment readily available, designating trained personnel to handle emergencies, and ensuring efficient communication within the healthcare team.
- Documentation and monitoring: Accurate documentation of Ryles tube insertion, patient response, and ongoing monitoring is essential. Regular assessments, including checking tube placement and monitoring patient tolerance and response to nutrition and medications, are necessary to ensure the ongoing appropriateness and safety of utilizing the Ryles tube in emergency situations.
The appropriate utilization of a Ryles tube in emergency situations can significantly impact patient outcomes and well-being. By enabling the delivery of nutrition and medications promptly and efficiently, the Ryles tube contributes to providing optimal care during critical moments.
Managing Bowel Obstruction with a Ryles Tube
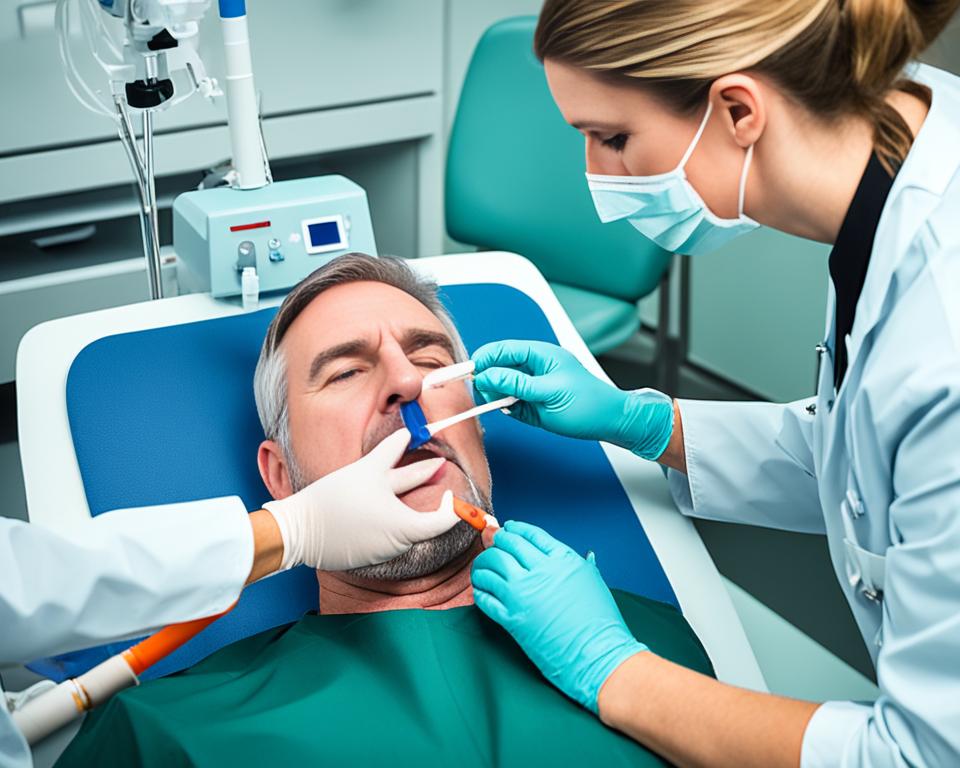
Bowel obstruction can be a challenging condition that requires prompt intervention. In cases where surgical intervention is not immediately feasible or necessary, a Ryles tube can play a crucial role in managing bowel obstruction by providing decompression and facilitating intestinal rest.
The procedure involves inserting a Ryles tube, also known as a nasogastric tube, through the nose or mouth and into the stomach. This tube allows for the removal of air and fluids from the gastrointestinal tract, relieving pressure and reducing the risk of further complications.
“The Ryles tube provides a non-invasive approach to manage bowel obstruction without resorting to surgery,” explains Dr. Rachel Johnson, a gastroenterologist at the XYZ Hospital. “By decompressing the gastrointestinal tract, the tube helps alleviate symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and vomiting.”
One of the key benefits of managing bowel obstruction with a Ryles tube is the promotion of intestinal rest. By reducing the workload of the bowel, the tube allows the intestines to heal and recover. This can help prevent the worsening of the obstruction and minimize the need for surgical intervention.
However, it is important to be aware of potential complications associated with the use of a Ryles tube for managing bowel obstruction. These complications may include tube displacement, aspiration, and infection. Close monitoring and proper care are essential to minimize the risks and ensure successful management.
To illustrate the benefits and considerations of managing bowel obstruction with a Ryles tube, refer to the table below:
| Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|
|
|
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional experienced in the management of bowel obstruction to determine the suitability and optimal approach for each individual case. They will assess the patient’s condition and provide appropriate guidance on the use of a Ryles tube for managing bowel obstruction.
Ryles Tube Insertion and Care Guidelines
In this section, we will provide comprehensive guidelines for the insertion and care of a Ryles tube. Whether you are a healthcare professional performing the procedure or a caregiver responsible for the ongoing maintenance of the tube, it is crucial to follow proper protocols to ensure the patient’s safety and well-being.
Insertion Guidelines:
- Prepare the necessary equipment, including a lubricant, measuring tape, Ryles tube, syringe, adhesive tape, and pH testing strips.
- Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain their consent.
- Position the patient in an upright or semi-upright position to facilitate the insertion process.
- Measure the length of the tube required for insertion. The measurement should be from the tip of the nose to the earlobe and then down to the xiphoid process.
- Lubricate the distal end of the Ryles tube to ease insertion.
- Ask the patient to tilt their head slightly forward and insert the tube gently through the nostril.
- Encourage the patient to swallow as the tube is passed through the pharynx and into the esophagus.
- Confirm correct placement by aspirating gastric contents and testing the pH. The pH should be acidic, indicating proper positioning within the stomach.
- Tape the tube securely to the patient’s nose to prevent accidental dislodgement.
Care Guidelines:
Proper care of the Ryles tube is essential to prevent complications and ensure effective functioning. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Check the tube for proper placement at regular intervals to ensure it remains securely positioned within the stomach.
- Flush the tube with water before and after each medication administration or feeding to maintain patency.
- Regularly assess the insertion site for signs of redness, swelling, or infection.
- Change the adhesive tape securing the tube as needed to maintain a secure and comfortable fit.
- Provide oral care to the patient to maintain oral hygiene and prevent complications such as oral thrush.
- Educate the patient and caregivers on proper tube care, including cleaning techniques and signs of potential issues.
Remember, always follow your healthcare facility’s specific protocols and consult with a healthcare professional for any concerns or questions regarding Ryles tube insertion and care.
Ryles Tube Removal and Aftercare
Once a Ryles tube has served its purpose and is no longer needed, the removal process is relatively straightforward. Here are the steps involved in safely removing a Ryles tube:
- Ensure that the healthcare professional performing the removal has washed their hands and put on clean gloves.
- Gently deflate any balloon or anchoring device attached to the Ryles tube, if present.
- While the patient is sitting upright or lying in a semi-reclined position, ask them to take a deep breath and hold it.
- With a quick and gentle motion, remove the Ryles tube from the patient’s nostril or mouth. It is important to be cautious and avoid any sudden or forceful movements to prevent injury or discomfort.
- Inspect the removed Ryles tube for any signs of damage or complications, such as tears or blockages. Document any relevant observations in the patient’s medical records.
Once the Ryles tube is successfully removed, it is crucial to provide proper aftercare to ensure the patient’s comfort and minimize any potential complications. Here are some guidelines for post-removal care:
- Encourage the patient to drink small sips of water or other fluids to soothe any discomfort or dryness in the throat or mouth.
- Advise the patient to consume soft and easily digestible foods for the first few meals following Ryles tube removal.
- Instruct the patient to monitor for any signs of abdominal pain, bloating, or changes in bowel movements, and to report any concerns to their healthcare provider.
- Provide information on proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing teeth and rinsing the mouth with mouthwash, to maintain good oral health.
- Offer emotional support and reassurance to the patient, as they may experience mixed feelings after the removal of the Ryles tube.
“Proper aftercare plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition for patients after the removal of a Ryles tube. By following these guidelines, healthcare providers can help patients recover comfortably and minimize any potential complications.”
Preventing Infections and Complications
Although Ryles tube removal is a relatively simple procedure, it is essential to take precautions to prevent infections and other complications. Here are some key measures to consider:
- Ensure that the healthcare professional performing the Ryles tube removal follows strict infection control protocols, including hand hygiene and the use of sterile gloves.
- Monitor the insertion site for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. If any abnormalities are observed, promptly notify the healthcare provider.
- Provide the patient with detailed instructions on keeping the removal site clean and dry, emphasizing the importance of proper hygiene.
Post-Removal Follow-Up
A follow-up appointment with the healthcare provider is recommended after Ryles tube removal to assess the patient’s condition and ensure a smooth transition. During this visit, the healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, address any concerns or questions the patient may have, and provide further guidance on dietary habits and oral care.
Overall, the removal of a Ryles tube marks an important milestone in a patient’s recovery. Proper post-removal care and follow-up support can contribute to a seamless transition and improved well-being.
Advancements in Ryles Tube Technology
The field of medical technology has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, revolutionizing the design and functionality of Ryles tubes. These advancements aim to enhance patient comfort, improve efficacy, and ultimately optimize patient outcomes. Let’s explore some of the notable advancements in Ryles tube technology:
1. Enhanced Comfort and Patient Experience
Newer designs of Ryles tubes prioritize patient comfort and convenience. Manufacturers have developed softer, more flexible materials that reduce discomfort during insertion and enhance overall tolerance. These advancements have made a significant impact on patient satisfaction and compliance with long-term usage.
2. Smaller Diameter and Improved Flexibility
Advances in materials science have enabled the production of Ryles tubes with smaller diameters and increased flexibility. These improvements have several benefits, including easier insertion, reduced risk of injury, and enhanced patient comfort. Additionally, these smaller tubes facilitate better tolerance and minimize post-procedural complications.
3. Anti-Clogging Mechanisms
Clogging of Ryles tubes can cause complications and hinder the effective administration of medications or nutrition. To address this issue, manufacturers have developed innovative anti-clogging mechanisms within the tube design, preventing blockages and ensuring consistent flow. This advancement reduces the need for frequent tube flushes and improves patient safety.
4. Integrated Gastric Residual Monitoring
Gastric residual monitoring is crucial in managing patients receiving enteral feeding through a Ryles tube. Recent advancements have seen the integration of sensors within the tube itself to measure and monitor gastric residuals accurately. This innovation allows healthcare professionals to optimize feeding regimens and minimize the risk of complications associated with inadequate digestion and absorption.
5. Tube Position Verification Systems
Incorrect tube placement can lead to serious complications, such as aspiration or respiratory distress. To overcome this challenge, advanced Ryles tubes now incorporate position verification systems. These systems utilize either pH measurement or electromagnetic technology to ensure correct tube placement in the stomach, providing healthcare professionals with added confidence and accuracy.
These advancements in Ryles tube technology represent a significant step forward in improving patient care and outcomes. However, it’s important to note that these innovations should be implemented under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective usage. The continuous pursuit of advancements in this field holds tremendous promise for further enhancing patient experience and optimizing medical care.
| Advancement | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Comfort and Patient Experience | Newer designs prioritize patient comfort and convenience, with softer and more flexible materials for reduced discomfort during insertion. |
| Smaller Diameter and Improved Flexibility | Advances in materials science enable the production of smaller diameter Ryles tubes, enhancing ease of insertion and patient comfort. |
| Anti-Clogging Mechanisms | Innovative designs incorporate anti-clogging mechanisms in the tube, preventing blockages and ensuring consistent flow. |
| Integrated Gastric Residual Monitoring | Ryles tubes now feature sensors for accurate measurement and monitoring of gastric residuals, allowing for optimized feeding regimens. |
| Tube Position Verification Systems | Ryles tubes incorporate position verification systems using pH measurement or electromagnetic technology to ensure correct tube placement. |
Patient Education and Ryles Tube Support

When it comes to patients who require a Ryles tube, providing comprehensive education and support is crucial for their well-being and successful treatment. Patient education plays a vital role in empowering individuals to actively participate in their care and understand the benefits and considerations associated with using a Ryles tube. By equipping patients with the necessary knowledge, they can make informed decisions and actively engage in their treatment journey.
One essential aspect of patient education is ensuring patients’ comfort with the Ryles tube. This involves explaining the purpose of the tube, how it works, and addressing any concerns or anxieties they may have. It is important to create a safe and open environment where patients feel comfortable asking questions and expressing their feelings. By actively listening and empathizing with patients, healthcare professionals can alleviate fears and build trust, fostering a sense of collaboration and support.
“Education is the key to empowerment. By providing patients with information and support, we enable them to take control of their own health and well-being.”
Aside from addressing patient concerns, educating patients on the practical aspects of Ryles tube care is essential. This includes teaching patients how to properly clean and maintain the tube, recognizing signs of infection or complications, and emphasizing the importance of regular check-ups and follow-up appointments. By providing clear and concise instructions, patients can confidently manage their tube and minimize the risk of complications.
In addition to personalized education, support groups and online resources can be valuable tools for patients with a Ryles tube. These platforms allow individuals to connect with others who are undergoing a similar experience, share insights, and seek guidance. Support groups foster a sense of community, reducing feelings of isolation and providing a safe space for open discussions. Online resources, such as educational materials and videos, can also reinforce patient education and serve as an additional source of information and support.
Key Strategies for Patient Education and Support:
- Listen actively and address patient concerns with empathy
- Provide clear instructions on Ryles tube care and maintenance
- Emphasize the importance of regular check-ups and follow-up appointments
- Offer educational materials and resources tailored to individual needs
- Encourage participation in support groups and online communities
By prioritizing patient education and support, healthcare professionals can empower individuals utilizing a Ryles tube to actively engage in their care, achieve better outcomes, and enhance their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Ryles tube is an invaluable medical device with a wide range of applications in healthcare. Its versatility allows for various interventions that significantly improve patient care and well-being.
The uses of the Ryles tube extend beyond just feeding and medication delivery. It plays a crucial role in gastric decompression, enabling the removal of excess fluids and air from the stomach. This intervention can provide relief to patients experiencing gastric distension and aid in their recovery.
Furthermore, the Ryles tube facilitates the monitoring of gastric residuals, helping healthcare professionals make informed decisions about feeding regimens and assess gastrointestinal motility. This monitoring technique can contribute to more personalized and effective patient care.
Overall, the benefits of the Ryles tube are evident in its ability to enhance patient outcomes and quality of life. With ongoing advancements and innovations in Ryles tube technology, we can expect even greater improvements in patient care in the future. The Ryles tube continues to be an essential tool in the healthcare setting, empowering healthcare professionals to provide optimal care to individuals in need of these interventions.
FAQ
What are the uses of a Ryles tube?
A Ryles tube is used for various purposes in medical care. It is primarily employed for feeding patients who are unable to eat or swallow, delivering medication and supplements directly into the stomach, decompressing the stomach to alleviate gastric distension, monitoring gastric residuals to assess gastrointestinal motility, managing bowel obstruction, and providing emergency support in situations where oral intake is not possible or immediate medication administration is required.
How is feeding done through a Ryles tube?
Feeding through a Ryles tube involves the insertion of the tube into the patient’s stomach, followed by the administration of liquid nutrition or formula directly into the stomach through the tube. Proper care and maintenance of the tube are essential to ensure successful feeding and prevent complications.
How is medication delivered via a Ryles tube?
Medication delivery via a Ryles tube involves the administration of medications or supplements directly into the patient’s stomach through the tube. This method is advantageous for patients who are unable to swallow or tolerate oral medications. It is important to follow proper guidelines and considerations for safe and effective medication delivery.
What is gastric decompression with a Ryles tube?
Gastric decompression with a Ryles tube is a procedure that involves the insertion of the tube into the stomach to remove excess air or fluids, relieving gastric distension and discomfort. This procedure is typically performed to alleviate symptoms associated with gastrointestinal conditions and can help improve the patient’s overall well-being.
How is monitoring gastric residuals done using a Ryles tube?
Monitoring gastric residuals using a Ryles tube involves the measurement and assessment of the amount of fluid or food remaining in the stomach. This helps healthcare professionals adjust feeding regimens and evaluate gastrointestinal motility. Monitoring gastric residuals is an important clinical practice that aids in optimal patient care.
In what emergency situations is a Ryles tube utilized?
A Ryles tube is utilized in emergency situations such as when a patient is unable to tolerate oral intake or requires immediate administration of medication. The tube provides a safe and efficient method of ensuring essential nutrition and medication delivery during critical times.
How does a Ryles tube help manage bowel obstruction?
A Ryles tube can assist in managing bowel obstruction by providing decompression and facilitating intestinal rest. This intervention reduces symptoms associated with bowel obstruction and promotes the return of normal gastrointestinal function. Proper insertion and care guidelines should be followed to ensure safe and effective use of the tube.
What are the guidelines for Ryles tube insertion and care?
Ryles tube insertion and care require adherence to specific guidelines. The proper steps for insertion should be followed, including ensuring correct tube placement and securing the tube in place. Maintenance and troubleshooting should also be conducted regularly to prevent complications and ensure the tube functions effectively. Patient education on tube care is crucial for promoting successful outcomes.
How is a Ryles tube removed and what care is needed afterward?
Removing a Ryles tube involves gently pulling the tube out of the patient’s stomach. After removal, care is needed to ensure the patient’s comfort and prevent complications. Close monitoring for complications and ensuring proper oral intake are essential during the post-removal period.
What are the advancements in Ryles tube technology?
Ryles tube technology has seen advancements in recent years, aimed at enhancing patient experience and outcomes. These advancements include the development of more comfortable and efficient tube designs, which offer improved functionality and ease of use. Ongoing advancements in the field promise potential future enhancements to further optimize patient care.
How important is patient education and support for individuals using a Ryles tube?
Patient education and support are crucial for individuals using a Ryles tube. Comprehensive education empowers patients to understand the device, effectively care for it, and address any concerns or questions they may have. Ensuring their comfort and providing ongoing support contribute to their overall well-being and successful tube utilization.