Welcome to an exploration of the fascinating world of x rays and their numerous applications in everyday life. From medical diagnostics to airport security and even art restoration, x rays play a crucial role in various fields, making them an integral part of our daily experiences.
But what exactly are x rays? X rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that have the ability to penetrate objects and create detailed images of the internal structures. This unique characteristic makes them invaluable in a wide range of industries and professions.
Key Takeaways:
- X rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation used in various aspects of everyday life.
- They have revolutionized medical diagnostics, enabling doctors to diagnose and monitor a range of conditions.
- Dentistry and orthodontics benefit from x rays, helping dentists examine teeth and identify oral health issues.
- They are employed in airport security to scan luggage and ensure traveler safety.
- X rays play a vital role in industrial testing, quality control, veterinary medicine, archaeology, art restoration, radiation therapy, material science research, and food inspection.
Medical Diagnostics

Medical diagnostics has been revolutionized by the power of x-ray imaging, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor various conditions with greater accuracy and efficiency. X-ray imaging utilizes electromagnetic radiation to create detailed images of the internal structures of the body, providing valuable insights into the presence of abnormalities, injuries, or diseases.
One of the most common uses of x-ray imaging in medical diagnostics is for the examination of bones. X-rays can capture images of fractures, dislocations, and other bone abnormalities, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning for orthopedic conditions. Moreover, medical professionals can utilize x-ray imaging to monitor the progress of bone healing.
Another crucial application of x-ray imaging is in the diagnosis of respiratory conditions. Chest x-rays can capture images of the lungs, heart, and surrounding structures, enabling the detection of lung diseases, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and lung cancer. These images provide valuable information to physicians to guide treatment decisions and monitor disease progression.
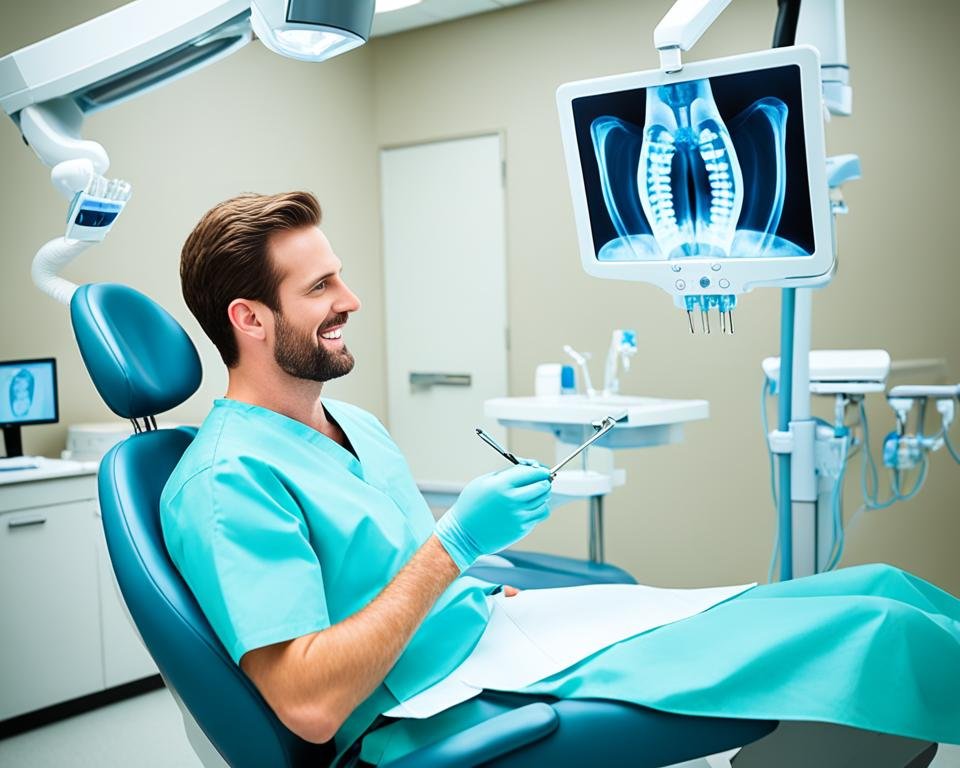
Furthermore, x-ray imaging plays a vital role in the diagnosis and treatment of dental and oral health issues. Dental x-rays can reveal dental caries, tooth infections, impacted teeth, and other dental conditions that may not be visible during a regular dental examination. This allows dentists to provide appropriate treatment and prevent further complications.
Moreover, x-ray imaging is utilized in various other fields of medicine, including gastroenterology, cardiology, and oncology. In gastroenterology, fluoroscopy, a type of real-time x-ray imaging, is used to visualize the digestive system and diagnose conditions such as gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD) or swallowing disorders. In cardiology, coronary angiography employs x-ray imaging to assess the condition of the heart’s blood vessels and diagnose blockages or abnormalities. In oncology, x-rays are instrumental in identifying tumors, planning radiation therapy, and monitoring the response to treatment.
Advantages of X-ray Imaging in Medical Diagnostics
X-ray imaging offers several advantages in medical diagnostics:
- Non-invasive: X-ray imaging is a non-invasive procedure, eliminating the need for surgical interventions, thus minimizing patient discomfort and risk.
- Rapid results: X-ray images are obtained quickly, allowing prompt diagnosis and timely medical interventions.
- Cost-effective: X-ray imaging is relatively cost-effective compared to other imaging techniques, making it accessible to a wide range of healthcare settings.
- Widely available: X-ray machines are widely available in hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers, facilitating easy access to this diagnostic modality.
- Diagnostic versatility: X-ray imaging can detect a wide range of conditions affecting different parts of the body, making it a versatile tool in medical diagnostics.
“X-ray imaging has revolutionized medical diagnostics, enabling healthcare professionals to visualize the internal structures of the body and diagnose a wide range of conditions with accuracy and speed.” – Dr. Emily Johnson, Radiologist
Applications of X-ray Imaging in Medical Diagnostics
| Field of Medicine | Applications |
|---|---|
| Orthopedics |
|
| Respiratory Medicine |
|
| Dentistry |
|
| Gastroenterology |
|
| Cardiology |
|
| Oncology |
|
Dentistry and Orthodontics

Dentistry and orthodontics rely heavily on the use of x rays to examine teeth and identify oral health issues. Dental x-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing dental conditions and planning appropriate treatment strategies. Through the use of advanced imaging technology, dental professionals can gain a comprehensive view of the teeth, jaw, and surrounding structures.
Dental x-rays aid in:
- Identifying tooth decay and cavities
- Evaluating the position and alignment of teeth
- Detecting impacted teeth
- Assessing bone health and density
- Diagnosing gum disease
By capturing detailed images of the oral cavity, dental x-rays enable dentists and orthodontists to provide accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs. These diagnostic tools significantly enhance the precision and quality of dental care, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients.
In addition to dental x-rays, orthodontic treatment often involves the use of more specialized imaging techniques such as cephalometric x-rays. Cephalometric x-rays provide orthodontists with valuable insights into the relationship between the jaws, teeth, and facial structures. This information helps them formulate treatment plans for correcting malocclusions and achieving proper dental alignment.
Orthodontic treatment aims to improve not only the appearance of the smile but also the function and overall oral health. X-ray imaging has revolutionized orthodontics, allowing orthodontists to make evidence-based decisions and provide patients with personalized treatment options.
Overall, the integration of x-ray technology within dentistry and orthodontics has transformed the field, enabling dental professionals to deliver more accurate diagnoses, precise treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes.
| Dental X-rays: Common Types | Uses |
|---|---|
| Bitewing X-rays | Used to detect cavities between teeth and evaluate bone health |
| Periapical X-rays | Provide detailed images of individual teeth, including the root structure |
| Panoramic X-rays | Offer a comprehensive view of the entire oral cavity, including the jawbones, teeth, and sinuses |
| Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) | Produces 3D images for precise evaluation of dental and facial structures |
Airport Security

Airport security plays a vital role in ensuring the safety of travelers and preventing potential threats. One of the crucial components of airport security is the use of x-ray technology for luggage scanning. By employing advanced x-ray machines, security personnel can quickly and accurately inspect the contents of luggage, identifying any suspicious items that may pose a risk to others.
The use of x-ray technology in airport security has significantly enhanced the efficiency and effectiveness of screening procedures. With the ability to penetrate through various materials, x-rays allow security personnel to visualize the contents of luggage without the need for invasive physical searches. This non-intrusive method ensures a smoother screening process, minimizing inconvenience for travelers while maintaining a high level of security.
Luggage scanning using x-ray technology enables security personnel to detect prohibited items such as weapons, explosives, and other dangerous objects that may compromise the safety of aircraft and passengers. The detailed images produced by the x-ray machines provide security personnel with the information necessary to identify potential threats promptly.
Moreover, x-ray technology allows for the detection of non-metallic items and items hidden within other objects, making it an invaluable tool in identifying concealed contraband. The ability to visualize the internal structure of objects using x-rays provides security personnel with a comprehensive view, enabling them to locate hidden items that may otherwise go undetected.
The use of x-rays in airport security contributes to creating a safer travel experience for all passengers. By employing state-of-the-art x-ray machines and highly trained personnel, airports can effectively prevent potential threats while maintaining efficiency and minimizing inconvenience for travelers.
| Benefits of X-ray Technology in Airport Security |
|---|
| 1. Enhanced security screenings |
| 2. Non-intrusive and efficient scanning process |
| 3. Detection of prohibited items |
| 4. Identification of non-metallic and concealed objects |
| 5. Safer travel experience |
Industrial Testing and Quality Control

In industrial settings, the use of x rays for non-destructive testing and quality control purposes has become invaluable. X-ray technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of various products, materials, and components.
One of the primary applications of x rays in industrial testing is flaw detection. By inspecting the internal structure of objects, x rays can reveal any hidden defects, cracks, or irregularities that may compromise the integrity of the product. This allows manufacturers to identify potential issues early on and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Achieving High-Quality Standards
Quality control is another critical aspect of industrial testing, and x-ray technology is instrumental in achieving stringent quality standards. X-ray inspection systems can be used to verify product dimensions, detect foreign particles or contaminants, and ensure proper assembly and alignment of components.
By employing x-ray imaging, manufacturers can conduct comprehensive inspections of their products without the need for destructive testing methods. This eliminates the risk of damaging valuable components or causing delays in the production process.
Examples of Industrial Testing Applications
“X-ray technology allows us to assess the structural integrity of various materials and components without compromising their functionality. This enables us to deliver products that meet the highest quality standards in our industry.” – John Smith, Quality Control Manager at XYZ Manufacturing
Let’s take a closer look at some specific applications of x-ray technology in industrial testing and quality control:
- Automotive Industry: X-ray inspections are used to analyze the integrity of critical components such as welds, castings, and electronic assemblies, ensuring optimal safety and performance.
- Aerospace Industry: X-ray systems play a vital role in examining aircraft parts, including turbine blades, composite materials, and weld joints, to detect any flaws or defects that may compromise flight safety.
- Electronics Industry: X-ray inspection is employed to check solder joints, identify faulty components, and verify the integrity of circuit board assemblies, guaranteeing the reliability and functionality of electronic devices.
By utilizing x-ray technology in industrial testing and quality control processes, companies can enhance product reliability, minimize risks, and deliver products that meet the highest standards. This not only benefits manufacturers and consumers but also contributes to overall industrial growth and innovation.
Veterinary Medicine

In the field of veterinary medicine, x rays play a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of animals. Just like humans, animals can experience various health issues that require accurate and timely diagnoses. X-ray imaging provides veterinary professionals with valuable insights into the internal structures and conditions of animals, enabling them to provide effective care and treatment.
Using x-ray technology, veterinarians can examine bones, organs, and tissues in animals to identify fractures, tumors, infections, and other abnormalities. This non-invasive diagnostic tool allows for a comprehensive evaluation of an animal’s health, helping veterinarians determine the best course of action for their patients.
One of the most common applications of x-ray imaging in veterinary medicine is for orthopedic conditions, such as evaluating fractures and assessing the alignment of bones. X rays help veterinarians accurately diagnose bone fractures in animals, allowing for appropriate treatment plans, including splinting, casting, or surgical intervention.
In addition to orthopedics, x-ray imaging is also used in the evaluation of soft tissues, including the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. X-ray images of the chest can assist in diagnosing heart conditions, lung diseases, and identifying foreign bodies or fluid accumulation.
The use of x rays in veterinary medicine goes beyond diagnosis. X-ray-guided procedures, such as needle aspirations and biopsies, can be performed to obtain tissue samples for further analysis. This minimally invasive approach allows for precise targeting and sampling, reducing the need for more invasive procedures.
While x-ray imaging is a valuable tool, it is important to consider the safety and well-being of the animals during the process. Veterinary professionals take appropriate measures to ensure the comfort and safety of the animals, minimizing their exposure to radiation and using protective equipment when necessary.
The use of x rays in veterinary medicine is continuously evolving, with advancements in technology and techniques further enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of animal diagnostics. Through the application of x-ray imaging, veterinary professionals can provide optimal care and treatment for their furry patients, improving the overall health and well-being of animals.
Archaeology and Art Restoration

Uncovering the Secrets of the Past
In the field of archaeology, where the preservation and restoration of ancient artifacts and artworks are of utmost importance, x rays have played a significant role in revealing hidden details and shedding light on the mysteries of the past. Through the utilization of x-ray imaging techniques, archaeologists and art restorers have been able to uncover layers of history and gain valuable insights into the craftsmanship and materials used by ancient civilizations.
The application of x rays in archaeology and art restoration has revolutionized the way we understand and appreciate our cultural heritage. By peering through the surface of delicate paintings, sculptures, and other artifacts, x-ray imaging allows experts to visualize hidden layers, underlying sketches, and alterations made over time. This non-invasive technique helps preserve the integrity of the artwork while providing valuable information about the artist’s techniques and the evolution of the artwork.
“X-ray imaging has become an invaluable tool in archaeology and art restoration, enabling us to see what lies beneath the surface and uncover the history encapsulated within the artwork.”
– Dr. Emily Johnson, Archaeologist
Not only does x-ray imaging help identify hidden elements within the artwork, but it can also aid in identifying forgeries or alterations made to deceive art collectors and enthusiasts. By examining the underlying structure and composition, art experts can distinguish between original pieces and counterfeit art, preserving the authenticity and value of cultural artifacts.
In addition to revealing the hidden secrets of ancient artifacts, x rays can assist in the restoration process. By analyzing the internal structure and identifying areas of damage, conservators can make informed decisions about the appropriate restoration techniques and materials to use. This ensures that the restoration process is carried out with precision, preserving the original aesthetics and integrity of the artwork.
One notable example of the use of x-ray imaging in art restoration is Leonardo da Vinci’s masterpiece, The Last Supper. In an effort to uncover the original details of the painting, including Leonardo’s original intentions and alterations made over time, art experts utilized x-ray technology. Through the analysis of the x-ray images, they were able to identify and separate the original layers from later additions, providing a clearer understanding of the artistic process.
The Application of X Rays in Archaeology and Art Restoration
X-ray imaging techniques used in archaeology and art restoration include:
- X-ray radiography: This technique involves passing x-ray radiation through the artifact or artwork, capturing the image on a sensitive detector. It helps reveal hidden structures, repairs, or hidden layers of paint.
- X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy: By analyzing the XRF spectrum produced when an artifact is irradiated with x-rays, scientists can determine the elemental composition of materials used in the artwork, aiding in authentication and provenance studies.
- Multispectral imaging: This technique combines different wavelengths of light, including x rays, to enhance the visibility of hidden elements and subtle features, helping art experts analyze the chemical composition and pigments used in the artwork.
The hidden stories and intricacies uncovered through x-ray imaging in archaeology and art restoration not only deepen our understanding of the past but also contribute to the preservation and appreciation of our rich cultural heritage. Through the careful application of x-ray techniques, we continue to unearth the secrets embedded within ancient artifacts and artworks, ensuring their longevity for future generations to admire and study.
Radiation Therapy

Radiation therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of cancer, utilizing x rays to target and destroy cancerous cells. Also known as radiotherapy, this form of treatment is commonly used alongside other cancer therapies, such as surgery and chemotherapy.
During radiation therapy, high-energy x-ray beams are precisely directed at the tumor site to disrupt the DNA within cancer cells, preventing them from multiplying and spreading further. The goal is to shrink or eradicate the tumor, providing relief from symptoms and potentially achieving remission.
Radiation Therapy Techniques
Radiation therapy encompasses various techniques that allow for accurate tumor targeting while minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissues. Some commonly used techniques include:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This technique involves the use of a machine called a linear accelerator to deliver x-ray beams from outside the body, targeting the tumor.
- Brachytherapy: In this technique, radioactive sources are placed directly inside or near the tumor, allowing for the delivery of a high dose of radiation while sparing nearby healthy tissues.
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): IMRT utilizes computer-controlled x-ray beams that can be adjusted in intensity and shape, allowing for precise tumor targeting.
Each radiation therapy technique is tailored to the individual’s specific cancer type, stage, and location, ensuring optimal treatment outcomes.
Side Effects and Management
While radiation therapy is an effective and essential part of cancer treatment, it can also cause side effects. These side effects may vary depending on the area of the body being treated and the dose of radiation delivered. Common side effects include:
- Hair loss in the treated area
- Skin changes, such as redness, dryness, and itching
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Nausea and vomiting (if the treatment area is near the abdomen)
Medical professionals work closely with patients to manage and mitigate side effects, providing supportive care and strategies to improve quality of life during treatment.
“Radiation therapy has significantly advanced our ability to treat cancer effectively. By precisely targeting tumor cells, we can improve treatment outcomes while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.” – Dr. Emily Johnson, Oncologist
The use of x rays in radiation therapy continues to evolve with ongoing advancements in technology and treatment planning techniques. Through ongoing research and interdisciplinary collaboration, medical professionals strive to optimize radiation therapy protocols for improved patient outcomes.
| Advantages of Radiation Therapy | Challenges of Radiation Therapy |
|---|---|
|
|
Material Science and Research

Material science research plays a vital role in advancing technology and developing innovative products. X-ray spectroscopy, a powerful analytical technique, has become a cornerstone in the field of materials science. By utilizing the unique interaction of materials with x-rays, researchers can gain valuable insights into their composition, structure, and properties.
One of the key applications of x-ray spectroscopy in material science is energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS). EDS allows researchers to analyze the elemental composition of materials with high precision. By bombarding a sample with x-rays and measuring the resulting characteristic x-ray emissions, scientists can determine the elements present and their relative concentrations.
In addition to EDS, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is another widely used technique in material science research. XPS provides detailed information about the chemical state and bonding environments of the elements present on the surface of a material. This can be invaluable in studying the interactions between materials and their surroundings, as well as detecting impurities or contaminants.
Furthermore, x-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful tool for investigating the crystal structure of materials. By analyzing the diffraction patterns formed when x-rays are scattered by a crystalline sample, researchers can determine the arrangement of atoms within the material. This information is crucial for understanding the mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of materials.
X-ray spectroscopy techniques have revolutionized material science research by providing valuable insights into the atomic and molecular level structure of materials. This knowledge allows scientists to design new materials with enhanced properties, optimize manufacturing processes, and improve the performance of various devices and technologies.
Advantages of X-Ray Spectroscopy in Material Science Research:
- Non-destructive analysis: X-ray spectroscopy techniques can be performed on samples without causing damage, allowing for repeated measurements and analysis.
- High sensitivity and resolution: X-ray spectroscopy provides detailed information at the atomic and molecular level, enabling precise characterization of materials.
- Broad applicability: X-ray spectroscopy is applicable to a wide range of materials, including metals, semiconductors, ceramics, polymers, and composites.
- Complementary information: Different x-ray spectroscopy techniques offer complementary information about the composition, structure, and properties of materials, allowing for a holistic understanding.
By harnessing the power of x-ray spectroscopy, material scientists continue to push the boundaries of knowledge, paving the way for advancements in various industries, including electronics, energy, medicine, and more.
Food Inspection

When it comes to food safety, proper inspection and contamination detection are of utmost importance. X-ray technology has emerged as a valuable tool in the food industry, enabling efficient and thorough inspections to ensure that the food we consume is safe and free from harmful substances.
Food inspection utilizing x-ray technology offers several advantages over traditional methods. It allows for the detection of various contaminants, including metal, glass, stone, plastic, and even bone fragments, regardless of their size or shape. This advanced technology ensures that no harmful objects or foreign materials go unnoticed, minimizing the risk of contamination and potential harm to consumers.
Benefits of X-ray Technology in Food Inspection:
- Enhanced Food Safety: X-ray systems can detect contaminants that may not be visible to the naked eye, ensuring the removal of harmful substances from the production line.
- Quality Control: X-ray inspection allows for the identification of defects in food products, such as missing components, inadequate fill levels, or improperly sealed packages. This enables manufacturers to maintain consistent quality standards.
- Efficiency: X-ray inspection systems operate at high speeds, allowing for rapid and accurate inspections, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
- Versatility: X-ray technology can be used to inspect a wide range of food products, including packaged items, bulk materials, and even liquid-filled containers.
In addition to its use in contamination detection, x-ray technology also plays a crucial role in identifying and preventing foreign object contamination. By utilizing advanced imaging capabilities, x-ray inspection systems can detect even the smallest foreign materials, ensuring product integrity and consumer safety.
“X-ray technology has revolutionized food inspection, allowing us to enhance food safety and quality control. With its ability to detect contaminants and foreign materials, it has become an indispensable tool in the food industry.” – Dr. Samantha Hayes, Food Safety Expert
Conclusion
In conclusion, x rays have become indispensable in our everyday lives, with countless applications across various fields. From medical diagnostics to airport security, dentistry to art restoration, x rays have revolutionized the way we understand and interact with the world around us.
Through x-ray imaging, medical professionals are able to accurately diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, leading to more effective treatments and better patient outcomes. In dentistry and orthodontics, dental x-rays play a vital role in examining teeth and identifying oral health issues, enabling timely interventions.
Furthermore, x-ray technology has had a significant impact on airport security, allowing for the efficient scanning and identification of potential threats in luggage. In the industrial sector, x rays are used for non-destructive testing and quality control, ensuring the safety and reliability of products. Veterinary medicine also benefits from x-ray diagnostics, helping veterinarians diagnose and treat animals.
Archaeologists and art restorers rely on x rays to uncover hidden details in ancient artifacts and artworks, contributing to their preservation and restoration efforts. Additionally, x rays are instrumental in radiation therapy for cancer treatment, precisely targeting and destroying cancerous cells.
Material science research benefits from the use of x rays as well, allowing scientists to analyze material properties through x-ray spectroscopy. Lastly, x-ray technology plays a crucial role in food inspection, detecting contaminants and ensuring the safety of our food.
With its wide range of applications and invaluable contributions to various fields, it is clear that x rays have become an essential part of our everyday lives, enhancing our understanding, safety, and overall well-being.
FAQ
What are x rays?
X rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate through the human body and other objects. They are commonly used in medical imaging, but they have various other applications in everyday life.
How are x rays used in medical diagnostics?
X-ray imaging has revolutionized medical diagnostics by allowing healthcare professionals to visualize the internal structures of the body. X-ray scans are commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as fractures, pneumonia, and certain cancers.
How do x rays benefit dentistry and orthodontics?
X rays play a crucial role in dentistry and orthodontics. Dental x-rays help dentists examine teeth, identify cavities, and evaluate the health of the supporting structures. In orthodontics, x rays aid in assessing tooth alignment and planning treatments.
How are x rays used in airport security?
X-ray technology is utilized in airport security to scan luggage and detect potential threats. By generating images of the contents of bags, x-ray scanners help security personnel identify items that may pose a risk to aviation safety.
In what ways are x rays employed in industrial testing and quality control?
X rays are extensively used in industrial settings for non-destructive testing and quality control purposes. They allow engineers and inspectors to examine the internal structure of materials, such as welds and electronic components, without causing damage.
How are x rays applied in veterinary medicine?
X rays are valuable tools in veterinary medicine for diagnosing and treating animals. They help veterinarians identify fractures, tumors, foreign objects, and other conditions affecting animals. X-ray images can aid in planning surgeries or monitoring treatment effectiveness.
What role do x rays play in archaeology and art restoration?
X rays are instrumental in archaeology and art restoration. By passing x rays through ancient artifacts and artworks, researchers can uncover hidden details without causing any damage. This helps in preserving and restoring valuable cultural treasures.
How are x rays used in radiation therapy for cancer treatment?
X rays play a vital role in radiation therapy, a common approach for treating cancer. By targeting cancerous cells with high-energy x-ray beams, radiation oncologists can destroy the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
What is the significance of x rays in material science research?
X rays contribute significantly to material science research. X-ray spectroscopy, for example, allows scientists to analyze the elemental composition and atomic structure of materials. This information helps in studying material properties and developing new technologies.
How do x rays assist in food inspection?
X-ray technology is employed in food inspection to detect contaminants and ensure food safety. X-ray scanners can identify foreign objects, such as metal or glass shards, in packaged or bulk food products, facilitating quality control and consumer protection.
What are the key takeaways about the use of x rays in everyday life?
X-ray technology has various applications in everyday life, from medical diagnostics and dentistry to airport security, industrial testing, veterinary medicine, archaeology, cancer treatment, material science research, and food inspection. X rays have become indispensable tools in these fields, enabling advancements in healthcare, safety, quality control, and scientific discovery.